Fentanyl Module
-
IntroductionIntroduction
-
What is Fentanyl and Why Is It so Deadly?
-
Medical Use
-
How does Fentanyl Affect the Body?
-
Summary
-
EffectsWhat are the Effects of Fentanyl?
-
Respiratory Depression
-
Rapid Overdose
-
Long-term effects
-
How can Fentanyl Impact People With Other Medical Conditions?
-
Summary
-
OverdoseWhat are the Signs of a Fentanyl Overdose?
-
Is Fentanyl Overdose Reversible?
-
Action Plan!
-
Routes of Administration
-
Summary
-
RisksGeneral Risks
-
Risk Philosophy
-
Polysubstance Use and Fentanyl Use
-
How to Decrease your Risk
-
Drug Checking
-
Activity
-
Summary
-
TreatmentSubstitution Treatment
-
Heroin-Assisted Treatment
-
Resources for Risk Management
-
Summary
-
Last Remarks!
How does Fentanyl Affect the Body?
What is fentanyl and how does it impact our bodies?
Fentanyl is a highly fat-soluble synthetic opioid, making it easy for it to access the brain. Fentanyl is among the most potent (powerful) opioids, with a potency that is approximately 50 times higher than heroin.
PHARMACOKINETICS
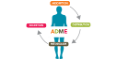
Definition: A series of processes that influence drug activity in the body.
Pharmacokinetics is divided into four parts:
Absorption, Distribution, Metabolism, Excretion (ADME)
ABSORPTION
- Refers to the process of the drug entering the blood from the administration site. This is influenced by how powerful the drug is (called: “potency”) and how it is entering the blood (called: the “route of administration”).
DISTRIBUTION
- Refers to the movement and balancing of the drug throughout the body.
METABOLISM
- Refers to the liver breaking down the drug to make it easier for it to exit the system.
EXCRETION
- This process refers to eliminating the drug from the body through urine or bile.
When injecting fentanyl, the drug travels quickly and gets distributed to the organs (e.g., the liver). It is then further redistributed to other areas such as muscle or fat tissues. Fentanyl can be distributed quickly because it is a very fat-soluble drug. Fentanyl gets broken down in the liver. Fentanyl is mostly excreted through the action of kidneys in the form of urine. It takes approximately 11-22 hours for fentanyl to leave your system.